Your Digestive System and How it Works
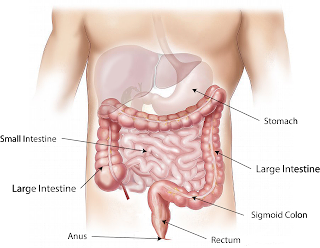
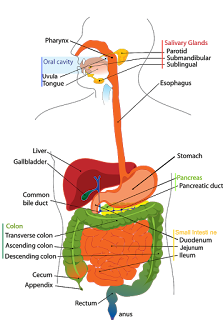
The stomach related framework is comprised of the gastrointestinal lot—likewise called the GI lot or stomach related parcel—and the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. The GI parcel is a progression of empty organs participated in a long, curving cylinder from the mouth to the rear-end. The empty organs that make up the GI lot are the mouth, throat, stomach, small digestive tract, digestive organ, and rear-end. The liver, pancreas, and gallbladder are the strong organs of the stomach related framework.
The small digestive tract has three sections. The initial segment is known as the duodenum. The jejunum is in the center and the ileum is toward the end. The internal organ incorporates the informative supplement, cecum, colon, and rectum. The informative supplement is a finger-formed pocket joined to the cecum. The cecum is the initial segment of the internal organ. The colon is straightaway. The rectum is the finish of the digestive organ.
Assimilation is significant on the grounds that your body needs supplements from food and drink to work appropriately and stay sound. Proteins, fats, sugars, nutrients NIH outside interface, minerals NIH outer connection, and water are supplements. Your stomach related framework breaks supplements into parts little enough for your body to ingest and use for energy, development, and cell fix.
 |
| The Digestive systems |
Proteins break into amino acids
Fats break into unsaturated fats and glycerol
Carbs break into basic sugars.
Food travels through your GI lot by an interaction called peristalsis. The huge, empty organs of your GI plot contain a layer of muscle that empowers their dividers to move. The development pushes food and fluid through your GI plot and blends the substance inside every organ. The muscle behind the food agreements and presses the food forward, while the muscle before the food unwinds to permit the food to move.
Mouth. Food begins to travel through your GI parcel when you eat. At the point when you swallow, your tongue drives the food into your throat. A little fold of tissue, called the epiglottis, folds over your windpipe to forestall gagging and the food passes into your throat.
Throat. When you start gulping, the interaction gets programmed. Your cerebrum flags the muscles of the throat and peristalsis starts.
Lower esophageal sphincter. At the point when food arrives at the finish of your throat, a ringlike muscle—called the lower esophageal sphincter — unwinds and allows food to pass into your stomach. This sphincter normally remains shut to hold what's in your stomach back from streaming once more into your throat.
Stomach. After food enters your stomach, the stomach muscles blend the food and fluid in with stomach related juices. The stomach gradually discharges its substance, called chyme, into your small digestive tract.
Small digestive tract. The muscles of the small digestive tract blend food in with stomach related juices from the pancreas, liver, and digestive system, and push the combination forward for additional assimilation. The dividers of the small digestive tract retain water and the processed supplements into your circulatory system. As peristalsis proceeds, the side-effects of the stomach related interaction move into the digestive organ.
Digestive organ. Byproducts from the stomach related cycle incorporate undigested pieces of food, liquid, and more seasoned cells from the coating of your GI parcel. The digestive organ assimilates water and changes the loss from fluid into stool. Peristalsis helps move the stool into your rectum.
Rectum. The lower end of your digestive organ, the rectum, stores stool until it pushes stool out of your butt during a defecation.
Limbzest384.blog.com